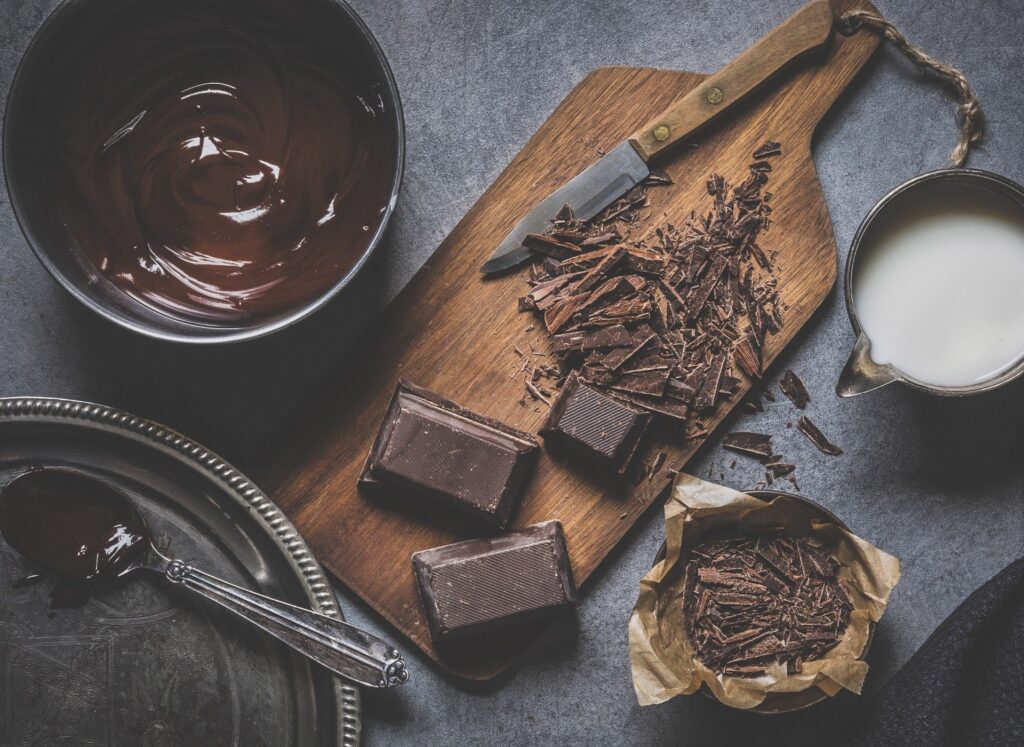
The global consumption of chocolate is nearly 1kg per capita every year. That’s a lot of chocolate! Yet, not everyone is aware what ingredients are found in their bar of chocolate.
When it comes to chocolate, less is usually more! A good bar of chocolate shouldn’t contain more than 3 to 4 ingredients.
In this post, we’ve listed out all the different ingredients you may find in a bar of chocolate.
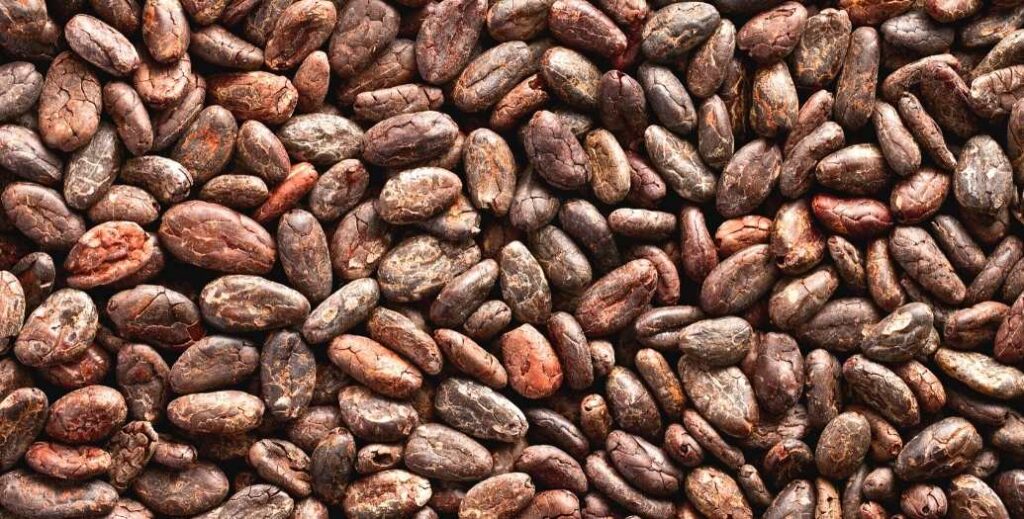

Cocoa or cacao
There’s one ingredient you cannot make chocolate without and that’s cacao (also known as cocoa). For chocolate to be qualified as chocolate it must contain a minimum amount of cocoa.
In the EU and UK a milk chocolate must contain a minimum of 35% cocoa solids for it to be legally sold as chocolate. A milk chocolate in the US must contain at least 10% cocoa solids.
Cocoa is derived from the fruit of the Theobroma cacao tree. These fruits, also known as cocoa pods, contain seeds which are fermented, dried, roasted, and eventually ground into chocolate liquor.
You may see cocoa stated on the list of ingredients as any of the following:
- Cocoa Beans
- Cocoa Mass
- Cocoa Solids
- Cocoa Liquor
When you see a percentage on a bar of chocolate (e.g. 70% dark chocolate) it refers to the percentage of cocoa in the chocolate bar. However, please note that this also refers to the amount of added cocoa butter in the chocolate.
If a dark chocolate is labeled as 80% cocoa, it may contain 70% cocoa beans and 10% added cocoa butter.
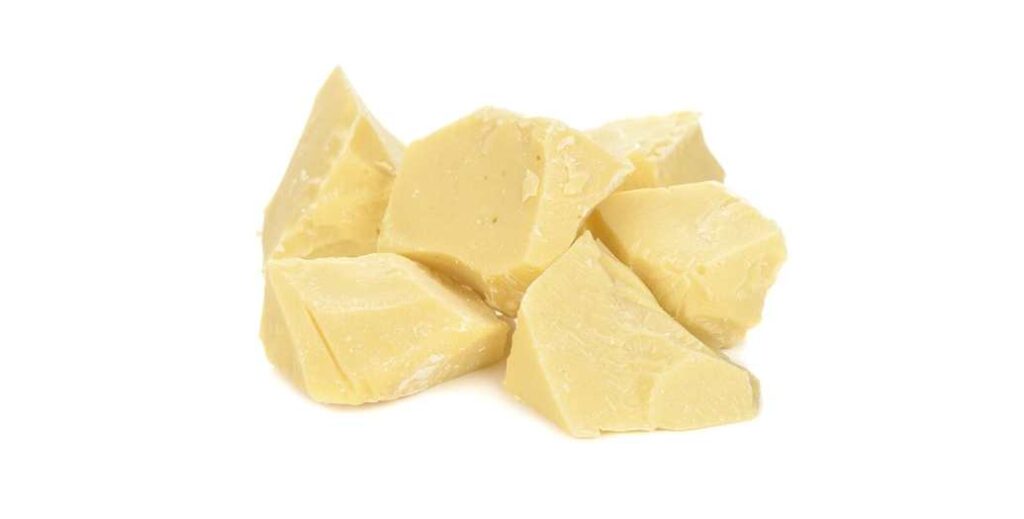

Cocoa butter
Cocoa butter (sometimes referred to as cacao butter) is a naturally occurring edible fat derived from cocoa beans.
This fat is extracted with the use of a hydraulic press, which applies large amounts of pressure onto cocoa liquor (ground up cocoa beans). This process separates out the cocoa butter, which has a pale yellow color.
Once extracted, the majority of cocoa butter is deodorized, which is a process of removing any taste and odors from the fat. Why is a lot of cocoa butter deodorized? Because a lot of it is used in cosmetics due to its richness in vitamins, minerals and antioxidants.
Many chocolate makers add cocoa butter into their chocolate in order to improve the texture whilst also making it easier to temper and work with.

Sugar
Sugar is a popular ingredient in chocolate. It turns the naturally bitter flavors of cocoa into a sweet treat.
The amount of sugar included in chocolate can vary greatly. Dark chocolate can contain between 20% to 40% sugar, whilst white and milk chocolate can contain 40% percent or more.
The type of sugar used will also impact the final flavor. Some varieties and names you might find are:
- White sugar (refined)
- Raw sugar (unrefined)
- Cane sugar
- Brown sugar
- Maple sugar
- Raw sugar
- Coconut sugar
- Caramelized sugar
These days sugar-free chocolate is becoming more popular. Sugar-free chocolate will either be made of 100% cocoa, or it’ll contain alternative sweeteners. These may include:
- Erythritol
- Stevia
- Xylitol
- Maltitol
- Polyglucitol

Milk (or mylk) solids
Milk solids, sometimes referred to as milk powder, is one of the main ingredients in milk and white chocolate. Because cows milk is naturally high in sugar it adds a sweet and creamy element.
Cow’s milk is the most common type of milk used in chocolate. However, there are more and more animal and plant-based alternatives from goat milk to oat milk. Alternative milk is sometimes referred to as mylk.
Different terms you might find include:
- Milk Powder
- Dried Milk Powder
- Dried Whole Milk
- Cow milk
- Ewe milk
- Goat milk
- Coconut milk
- Rice milk
- Almond milk
- Oat milk
- Soya milk
- Cashew milk
Milk, whether it’s animal or plant-based, is added as a powder during the chocolate making process. Because milk is a major allergen it will be both in bold and then often in parentheses on the chocolate bar packaging.

Lecithin
Lecithin is a food additive that’s used as an emulsifier in chocolate. It’s not an essential ingredient in chocolate. However, it helps bind the cocoa solids, sugar and milk to the cocoa butter. This ensures the chocolate is smooth whilst also reducing the chances of your chocolate blooming.
Lecithin is extracted from various sources including sunflower, rapeseed, soy, and even animal tissues. Because only a small amount is added to chocolate, it doesn’t affect the overall flavor.
Some common emulsifiers found in chocolate include:
- Soy lecithin
- Organic Soy lecithin
- Sunflower lecithin
- Rapeseed lecithin
- Vegetable lecithin

Vegetable fats
Vegetable fats are usually a sign of cheap and unhealthy chocolate. Why? Instead of containing the natural cocoa butter, cheap chocolate replaces it with vegetable fats such as palm oil.
Vegetable fats in chocolate are unpopular with bakers, chocolatiers, and pastry chefs as when you try to melt or bake with chocolate that’s made with added vegetable fats, the mix can separate and become grainy.
In the United States, a chocolate bar can’t be called ‘chocolate’ if it contains vegetable fats. Though chocolate companies can get around this by describing their products ‘chocolate flavored’, ‘chocolate-like’, and ‘chocolatey’. In the EU, chocolate makers can add up to 5% vegetable fats to their chocolate. Vegetable fats you might find in the ingredients of cheap chocolate includes:
- Vegetable oil
- Shea butter
- Palm oil
- Mango kernel
- Sal
- Kokum gurgi
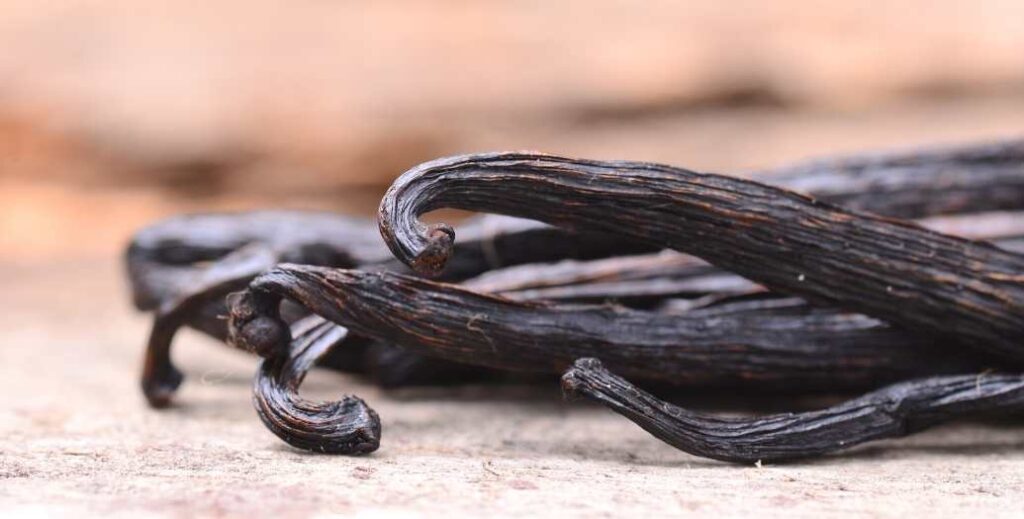

Vanilla
Vanilla has been a popular addition to chocolate for centuries. The vanilla orchid is native to modern-day Mexico and the Aztecs were known to add vanilla in their cacao beverages.
It’s easy to see why as well! The sweet flavors and fragrance of vanilla complement the bitter notes of cocoa. However, most vanilla found in chocolate today is not derived from natural vanilla.
In fact, over 95% of vanilla products sold globally contain natural vanilla at all. This is due to the limited supply and high price of natural vanilla pods. In recent decades synthetic varieties have been created from alternative materials (including wood shavings) to mimic the vanilla flavor we expect to taste.
These are some of the ways vanilla may be found on the ingredients list:
- Vanilla
- Vanillin
- Vanilla flavoring

Flavorings, colorings and inclusions
From whisky to raspberry, added flavors are a popular way of spicing up a bar of chocolate. Flavorings can be added in a few ways, but generally, drops of oil are used as they don’t change the texture of chocolate as much and only require a small amount.
Both natural and artificial colourings can be added to chocolate to change the color and appearance, this could be to outer shells (like smarties, or M&M’s) or to the chocolate itself. This is more common in white chocolate which is the easiest to color, and can be decorative or fully changed from an off-white to pink, orange, or something else.
Another way that chocolate makers use coloring in their chocolate is to mix it into tempered cocoa butter and paint transfers, molds or directly onto the chocolate to create a specific design.
Unlike flavorings, inclusions impact the texture of the bar of chocolate. This could be anything from cocoa nibs to sea salt to freeze-dried fruit. Just like with added flavorings, these are there to enhance or add to the experience of chocolate.